There’s no single best RAID configuration for all servers. The ideal choice depends on the balance you need between three main factors: performance (speed), redundancy (safety against disk failure), and cost/capacity .
## Most Common RAID Levels
Below are the most common RAID types and their best applications.
### RAID 0 (Stripping)
- How it works: Data is striped and written to all disks simultaneously.
- Advantages: 🚀 Maximum read and write performance . 100% use of total disk space.
- Disadvantages: 💀 No redundancy . If a single disk fails, all data on all disks is lost.
- Ideal for: Video editing, caching files, or any application where speed is crucial and data loss isn’t catastrophic (since it’s backed up elsewhere).
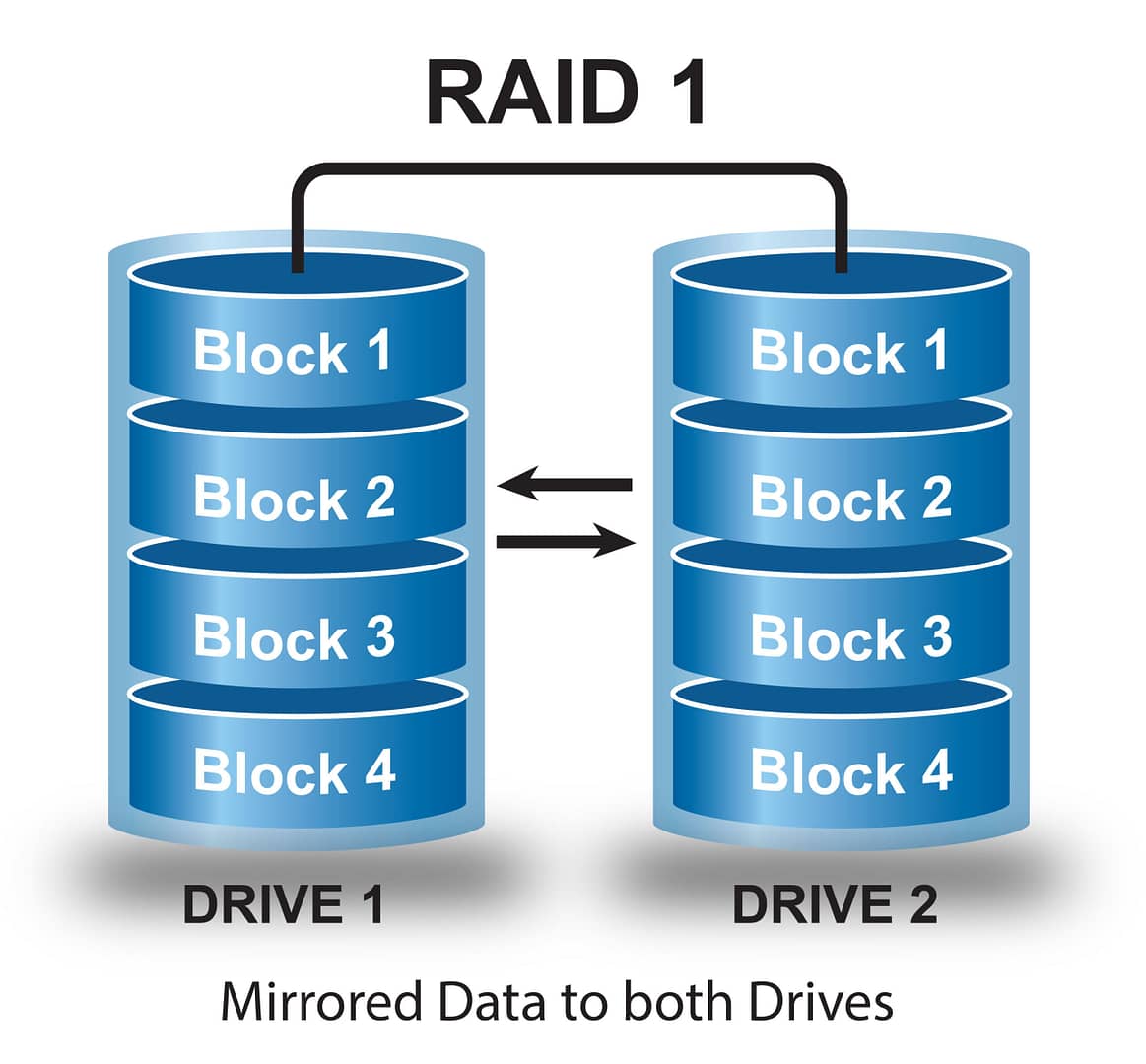
### RAID 1 (Mirroring)
- How it works: Data is duplicated. Everything written to one disk is mirrored on the other.
- Advantages: ✅ High redundancy . The system continues to operate normally even if a disk fails. Good read speed.
- Disadvantages: 💰 High cost . You can only use 50% of the total storage capacity (e.g., two 4TB disks result in only 4TB of usable space).
- Ideal for: Operating systems, small databases, and critical applications where availability is more important than capacity.
### RAID 5 (Stripping with Parity)
- How it works: Data is divided between disks (as in RAID 0), but “parity” information is also recorded that allows data to be reconstructed in the event of a failure.
- Advantages: 👍 Good balance between performance, capacity, and security. Tolerates disk failure .
- Disadvantages: Write performance is lower than read performance. The rebuild process (reconstructing data after replacing a disk) can be slow and overload other disks.
- Ideal for: File servers and general-purpose applications that need ample storage space with protection.
Attention: With very large disks (over 4TB), the RAID 5 rebuild time can be so long that the risk of a second disk failing during the process increases.For these cases, consider RAID 6 or RAID 10.
### RAID 6 (Stripping with Double Parity)
- How it works: Similar to RAID 5, but with twice the parity information.
- Advantages: 🔒 Very high redundancy . It tolerates the failure of up to two disks simultaneously, making it very safe.
- Disadvantages: Write performance is slower than RAID 5 due to the extra parity calculation.
- Ideal for: Critical data storage, long-term archiving, and backup servers where data security is a top priority.
### RAID 10 (or RAID 1+0)
- How it works: It’s a combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0. First, the disks are mirrored in pairs (RAID 1), and then the data is striped between these pairs (RAID 0).
- Advantages: 🏆 The best of both worlds: offers the excellent performance of RAID 0 and the high redundancy of RAID 1. Extremely fast rebuild.
- Disadvantages: 💸 Higher cost . Like RAID 1, you lose 50% of your total storage capacity. Requires at least 4 disks.
- Ideal for: High-performance databases, virtualization servers, and critical applications that require maximum speed and security.
### Quick Comparison Table
| RAID level | Min. Disks | Fault Tolerance | Performance (Writing) | Useful Capacity | Main Advantage |
| RAID 0 | 2 | 0 disks | Excellent | 100% | Speed |
| RAID 1 | 2 | 1 disk | Reasonable | 50% | Redundancy |
| RAID 5 | 3 | 1 disk | Good | (Number of Discs – 1) | Balance |
| RAID 6 | 4 | 2 disks | Reasonable | (Number of Discs – 2) | High security |
| RAID 10 | 4 | at least 1 disk | Excellent | 50% | Speed + Safety |
## Which one to choose? 🤔
- For server operating system: RAID 1 is the safest and most common choice.
- For a general file server: RAID 5 (with smaller disks) or RAID 6 (with larger disks) are great options.
- For a database or virtualization server: RAID 10 is the best choice, hands down, if budget allows.
- For temporary or low-importance data: RAID 0 can be used to maximize speed, as long as you have backups.